In this Post:
- What Does FICO Stand For?
- FICO Score: Explained
- Different Types of Credit Scores
- FICO Score vs. Vantagescore
- All About FICO Score Range Levels
- FICO Middle Score
- Average FICO Score
- How Does FICO Work?
- Factors That Impact FICO
- How to Obtain Your FICO Score
- Free FICO Score
- Regular Access to FICO
- FICO Score for Beginners
- Improving Your FICO score
- The Popularity of FICO
When you hear the term “credit score,” in many cases people are referring to the FICO credit score. It’s the most popular credit scoring model and is used by a majority of lenders. It’s not the only type of credit score but is the most widely used. What is FICO and what does it mean? Read on to learn the ins and outs of FICO.
The Most Common Questions About FICO
What is FICO? What does FICO stand for?
These are common questions if you’re just learning about credit scores.
FICO stands for Fair Isaac Corporation. The company was created in 1956 by founders Bill Fair and Earl Isaac — hence the name. Today FICO is a leading credit risk company that provides FICO scores. FICO scores are used in over 90% of lending decisions.
FICO Score: A Breakdown of What It Means
A FICO score is a type of credit score. Credit scores assess your level of risk and show lenders what type of borrower you are. The information in your credit report — which is a document that contains all of your credit and payment history — contributes to your credit score.
The standard FICO credit score model is a numerical range, typically from 300 to 850, though it should be noted there are various FICO models. In this case, a higher number reflects positively on the borrower and shows that they are “creditworthy.” A score on the lower end of the scale could mean the borrower has “poor” or “bad” credit.
Guess What? FICO Isn’t the Only Credit Score Company
Seeing as FICO in many cases is the default credit score you may wonder if FICO is the only credit score company. Though over 90%of lenders use FICO credit scores, there are actually numerous credit scoring companies. Even within the FICO system, there are different FICO scores depending on what you need. For example, there may be a FICO auto score if you’re looking to get a car loan.
Each credit score company has their own proprietary data. There are other popular credit score companies like Plus Score and VantageScore. VantageScore is similar to FICO — but not the same — and is used on many “free credit score” sites.
The Differences Between FICO and Vantagescore
FICO scores and VantageScores are pretty similar. In the past, VantageScore had a range of 501-900 but when they released VantageScore 3.0, they changed the range to mirror the FICO range. So the VantageScore 3.0 range is 300-850, just like the FICO range.
Regardless of the credit score model, whether FICO or VantageScore, higher numbers mean better credit and lower numbers mean poorer credit.
One main difference between the models is around credit history.
If you have a limited credit history, it can take up to six months to produce a score with FICO. However, it only takes one month of credit history to produce a VantageScore credit score. In this case, if you need a credit score to show a landlord or lender and have a limited credit history, a VantageScore credit score may be a better fit.
Another significant difference is how they treat late payments. Any way you put it, late payments are bad and can reflect poorly on your credit. But with VantageScore they penalize late mortgage payments more heavily compared to other types of late credit payments.
Aside from credit history and late payments, the biggest difference is that the majority of lenders use FICO, whereas VantageScore can be used more for consumers who want to know where their credit is at. However, according to VantageScore, 4.9 billion VantageScore credit scores were used by credit card issuers. So there definitely are lenders that use the VantageScore credit score model to evaluate creditworthiness.
What Differentiates a Good FICO Score from a Bad One?
So you know the FICO score range but what differentiates a bad FICO score and a good FICO score?
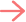
It’s a bit nuanced. There are five FICO credit score designations along with their own ranges:
What are the levels of FICO scores?
So a “good FICO score” is essentially 670 or above. You can get the best rates with a good credit score and have higher chances at approval when applying for credit. If you’re looking to get a mortgage, having a credit score of 660 or higher can help you get approved.
There’s Also a FICO Middle Score. Here’s Where It Is.
At some point you might hear the term “FICO middle score.” What? Yet another score! It can be confusing.
Your FICO middle score is typically used when applying for a mortgage. There are three credit bureaus: Experian; TransUnion; and Equifax. Each one of them have a different FICO score for you. Why? This is because not all lenders and creditors report to all of the credit bureaus, so each bureau may have different info that contributes to your score.
So, a mortgage lender will take a look at the three FICO scores produced by the credit bureaus and pick the middle number.
Let’s say your FICO credit scores are:
- 710
- 690
- 720
In ascending order, 710 would be the middle score that a mortgage lender would use.
What Is the Average FICO Score and Does It Matter?
The FICO score model has a big range — from 300 to 850. As a consumer you might wonder what the average FICO score is for consumers. As of September 2018, the average FICO credit score was 704.
So the average FICO score is good, but you have to remember that averages are created from the lowest and highest numbers within a group. If your credit score is not the “average FICO score” don’t fret; just keep working on building your credit with a positive repayment history.
How Is a FICO Score Determined?
FICO scores aren’t just created arbitrarily. You’re likely wondering “How does the FICO score work?” The number that is created for your FICO credit score is based on the information in your credit report.
Your credit report shows your credit accounts, payment history, inquiries, as well as any liens or judgements. Based on that information, FICO will create a number that illustrates your creditworthiness for lenders to use for review.
5 Factors That Impact Your FICO Score
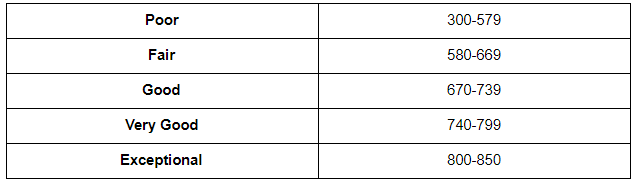
The information in your credit report helps form the FICO score. However, there are a number of specific factors that affect your FICO score. Here are the five factors and the percentages that make up your credit score.
Payment history — 35%
Credit utilization — 30%
Length of credit history — 15%
New inquiries — 10%
Credit Mix — 10%
Your payment history by far has the greatest impact on your credit score. Second to that is your credit utilization, which refers to the amount of your credit limit that you use. The length of credit history refers to how long you’ve been a borrower of credit.
New inquiries refers to how many applications you have for new credit. If you apply for a new line of credit, there will be a “hard inquiry” on your credit report. Having too many inquiries in a short amount of time can seem like you over rely on credit and that looks risky to a lender.
Credit mix refers to the various types of credit you may have from real estate, student loans, or credit cards. Having a diverse credit portfolio can reflect well on the borrower.
In order to get into the 800s, all factors must be in good shape. For example, if you don’t have a diverse credit portfolio, your credit mix won’t be great and can hurt your score. You can focus on having both installment loans and revolving credit in your portfolio. If it’s about the length of your credit history, you want to make sure to keep your accounts open.
In other words, getting the best of the best FICO scores require all five components to work together.
Want to Obtain Your FICO Score? Here’s How.
If you want to know your FICO credit score, it’s not something you can really figure out on your own. How can you obtain a FICO credit score? You can check your FICO credit score through the FICO website or their partners’ sites like MyFICO, Experian, and Equifax.
It’s Possible to Access Your FICO Score for Free!
Getting your official FICO credit score through the channels listed above is possible. However in some cases you may have to pay to access your FICO credit score.
What if you want your FICO score for free? You may get your free FICO score with your credit card issuer, in some cases, or from your financial institution.
Regular Access to Your FICO Score May Cost Money
Though getting your FICO score free can be great, if you want to regularly access your FICO credit score you may be better off paying for access through one of the FICO-affiliated sites.
What’s a Typical Starting FICO Score?
If you're interested in building credit and just getting started you may be curious and think, “What will my starting FICO score be?”
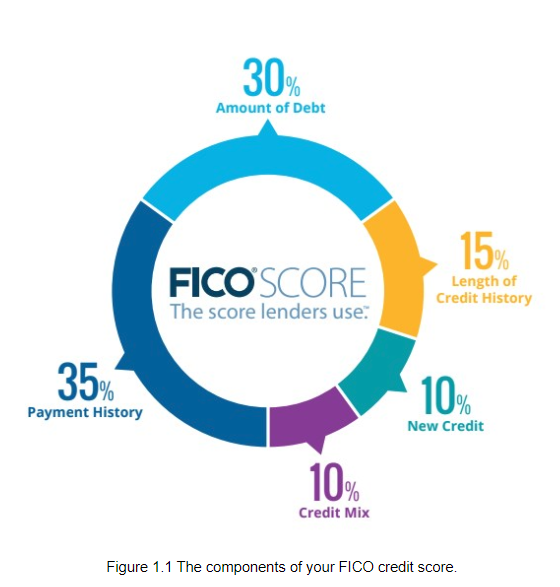
This can depend. As noted above, it can take up to six months for a FICO score to be produced from your credit history. A credit score of 300 is the lowest level. If you have at least one loan or type of credit card, and make payments on time, it will likely be in the Fair to Good range. It’s not possible to have a credit score of 0.
No credit score means no credit history.
If you have some credit history, you will have a score that you can build upon.
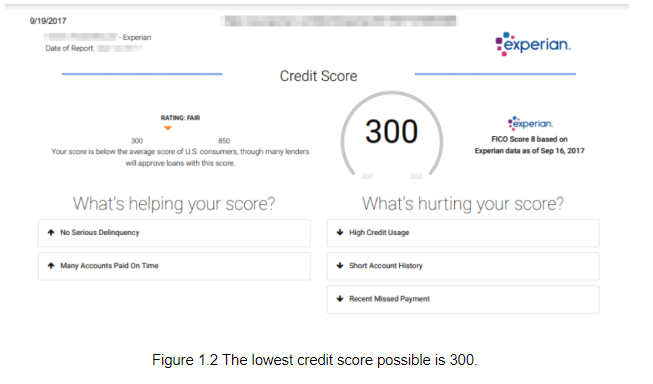
Here's How to Improve Your FICO Score
If you have a poor FICO credit score it may be hard to get approved for any credit. But your situation is not hopeless though. You can improve your FICO credit score. You may wonder,
“How do I improve my FICO score, really?”
Based on the FICO score chart above you can see that your payment history and credit utilization are the most significant factors when it comes to your credit. Start by paying all of your bills on time! You also want to keep you balances low. Keeping your credit utilization below 30%may help improve FICO score.
Also be mindful of only borrowing what you need. Don’t apply for too many forms of credit. That can look like risky behavior to a lender.
The biggest takeaway is to make your payments on time.
FICO Scores Reign Supreme
Now you know there are various types of credit scores, but FICO scores still reign supreme. FICO scores are used by many lenders to determine if you are a good candidate or not, so it’s something helpful to know before applying for credit.